Protect Your Data: Essential Strategies for Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
April 5, 2024
In the private equity sector, the importance of data security cannot be overstated. As digital data becomes integral to business operations, the risk of data loss is a pressing reality for firms of all sizes. Protecting against data loss is not merely necessary but a fundamental of organisational resilience. Prioritising data loss prevention (DLP) strategies is essential to protect your investments and maintain stakeholder trust.
There are numerous risks, from accidental deletions to sophisticated cyberattacks. Understanding these threats and implementing effective countermeasures is not just a technical requirement but a strategic imperative. The consequences of data loss extend beyond financial setbacks, affecting reputational integrity, legal compliance, and overall business continuity.
The impact of data loss can be catastrophic, potentially crippling a business. On average, it takes over 280 days to detect and mitigate a data breach. The consequences of such an event are undeniably severe:
 This comprehensive guide will explore essential DLP strategies, from fundamental best practices to advanced data protection techniques, making it easier for private equity firms to understand and implement effective data loss prevention measures.
This comprehensive guide will explore essential DLP strategies, from fundamental best practices to advanced data protection techniques, making it easier for private equity firms to understand and implement effective data loss prevention measures.
Data loss prevention (DLP) refers to a set of tools and methodologies designed to protect sensitive data from accidental loss, misuse, or unauthorised access. It is a critical component for private equity firms aiming to maintain data integrity and comply with regulatory standards.
At its core, DLP protects organisations from the dual threats of data loss and data leakage. Data loss, often caused by ransomware attacks, involves the irreversible loss of crucial organisational data. DLP is primarily focused on preventing the unauthorised exfiltration of data beyond the organisation’s boundaries.
Data leaks can cause significant organisational distress and stem from various sources, each posing distinct threats to data integrity. Here are four main culprits:
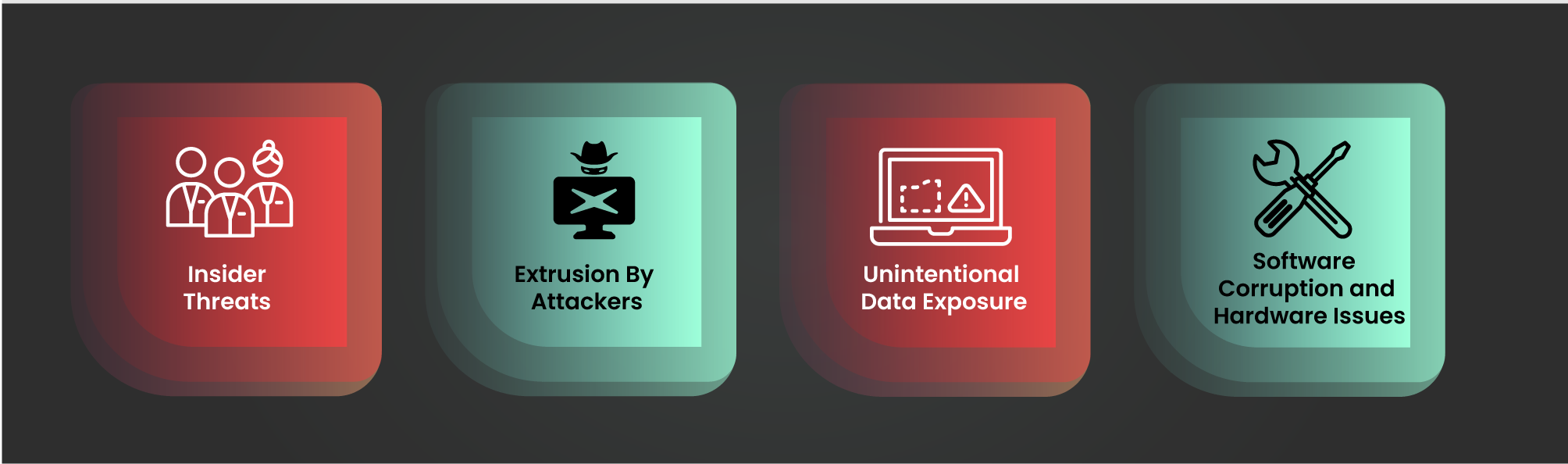
To effectively prevent data loss, it’s essential to implement a set of best practices that address the various causes of data loss. Here are some key strategies:
Identify and categorise the various types of data your organisation handles based on their sensitivity and value. This helps prioritise efforts and allocate resources effectively to protect critical data.
Encryption converts data into a code, accessible only with a decryption key. It’s a powerful tool for securing sensitive information from cyber threats. By applying complex algorithms, encryption transforms data into an indecipherable format, which can only be decoded with the corresponding decryption key.
This process adds an extra layer of protection to critical data, including financial records and customer information, whether it’s stored or transmitted. Compliance with data security standards like PCI DSS and GDPR often mandates encryption to prevent breaches and regulatory violations.
Using encryption, such as the Encrypting File System (EFS) in Windows, ensures that only authorised users can access or modify files. Even if a device is compromised, unauthorised users won’t be able to decipher the encrypted data, significantly reducing the risk of data loss.
Limiting user access to essential data is a highly effective method for preventing data loss. By granting access only to the data necessary for their role, organisations can minimise the risk of unauthorised access and inadvertent data exposure.
If additional access is required, users can request permission from designated personnel, who can grant access temporarily and with limitations. This approach enhances data security by ensuring that access privileges are granted judiciously and in line with business needs.
Ensure your operating system is as secure as possible. Remove any unnecessary apps and services that may create vulnerabilities. Consider creating a baseline image of your operating system for employees, enabling additional functionality only when necessary.
Avoid storing unnecessary data, as it can lead to false positives, making it harder to protect valuable information.
Monitoring data access is crucial for protecting sensitive information. By tracking who accesses data, when, and how, organisations can swiftly detect and address breaches, preventing further unauthorised access.
Methods for monitoring data access include:
Effective data access monitoring enables prompt responses to breaches, minimising their impact and preventing further unauthorised access. This practice also aligns with various data security standards and regulations, including PCI DSS.
Maintaining up-to-date systems is essential to prevent zero-day vulnerabilities and other cyberattacks that could result in data loss. Regularly update operating systems, applications, firmware, and other software components.
While updates are often automated, using an automated patch management solution can provide greater visibility into the installation process, including what patches are being installed, when, how, and why.
Regular security audits are essential for a robust Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategy. These audits involve a thorough examination of an organisation’s security policies, procedures, and controls to identify vulnerabilities. By conducting these audits regularly, organisations can proactively secure their data assets and reduce the risk of data breaches.
During a security audit, various aspects of an organisation’s security posture are evaluated, including software, hardware, network infrastructure, and security policies. The goal is to uncover weaknesses or gaps that could be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorised access to sensitive data.
Once vulnerabilities are identified, organisations can promptly take remedial actions. This may involve patching software, updating hardware configurations, enhancing network security, or refining security policies. Addressing these vulnerabilities proactively significantly reduces the risk of data loss incidents.
Furthermore, regular security audits help organisations ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards like PCI DSS and GDPR. These regulations often mandate regular security assessments, demonstrating the organisation’s commitment to protecting sensitive information and maintaining trust.
Providing regular security awareness training to all employees is crucial for preventing data loss due to human error. Employees should be trained to recognise suspicious emails, SMS messages, and phone calls, create strong passwords, and use multi-factor authentication.
In addition to training employees on best practices, organisations should establish clear policies and procedures for data handling and access control. This includes guidelines for handling sensitive data, such as using encrypted storage devices and avoiding the use of personal email accounts for work-related activities.
Implementing incident response procedures is essential for organisations to effectively manage data breaches. Despite preventive measures, breaches can occur due to unforeseen vulnerabilities or persistent attackers. Therefore, a robust incident response plan is necessary.
Key Steps in an Incident Response Plan:
A well-prepared incident response plan enables organisations to mitigate breach impacts, address legal obligations, and resume normal operations swiftly.
Adhering to the 3-2-1 backup strategy is crucial for protecting your data against permanent loss. This strategy entails:
This rule serves as a robust guideline for data protection, ensuring redundancy, resilience, and the ability to recover data even in the face of unexpected events or disasters.
By mitigating single points of failure, enhancing data availability, and protecting against corruption, redundancy ensures the safety of critical information. It plays a critical role in disaster recovery, adapting to evolving technologies, and meeting compliance requirements. Diversified storage and off-site backups, as recommended by the rule, effectively mitigate various risks, contributing to the overall security and reliability of critical data.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is highly versatile, adapting to an organisation’s specific needs and regulatory requirements. This adaptability makes DLP indispensable for organisations operating in jurisdictions with varying data protection laws. It plays a crucial role in helping organisations comply with data protection regulations by preventing breaches such as ransomware and phishing.
For example under GDPR, organisations must ensure personal data is not wrongfully accessed or shared. DLP solutions can identify GDPR-protected data, such as personal identifiers, and control its handling and access, demonstrating a commitment to compliance.
In sectors dealing with financial information, like banking or online retail, DLP aids in adhering to regulations like PCI DSS by securing financial data. DLP is more than just blocking data transfers; it’s about understanding data flows, identifying risks, and ensuring data handling aligns with compliance requirements.
Establishing a robust culture of data security is essential for effectively preventing data loss. This involves promoting an environment where every member of the organisation understands the importance of data protection and actively participates in the security process.
Here’s how organisations can cultivate such a culture:
Data protection is essential for trust and reliability in the private equity sector. The challenges of data security are constantly changing. private equity firms must be proactive, vigilant, and innovative in protecting their data assets and maintaining investor confidence.
By prioritising Data Loss Prevention (DLP), firms can protect their valuable data, comply with regulatory standards, and uphold their reputation and trustworthiness among investorss and stakeholders.
Expert guidance and advanced solutions in data protection are crucial. We specialise in bespoke data protection solutions for private equity firms. Our expertise spans risk assessment, cutting-edge cyber security technologies, and ongoing support and guidance. Ensure your firm is protected and ahead in data security. Contact OneCollab today for a Comprehensive Evaluation.
Cyber security shouldn’t be a headache. Get clear and actionable insights delivered straight to your inbox. We make complex threats understandable, empowering you to make informed decisions and protect your business.
Call us +44 20 8126 8620
Email us [email protected]