Introduction
Human error in cyber security is a significant concern. As organisations navigate the complexities of protecting their digital assets, understanding the impact of human factors is crucial. Verizon’s 2023 report highlights that 74% of all breaches involved a human element, revealing the vulnerabilities linked to lapses in judgment or oversight.
This article simplifies the complexities of human error in cyber security, helping you understand its implications and secure your data through proactive measures.
The Alarming Statistics: A Wake-Up Call for Businesses
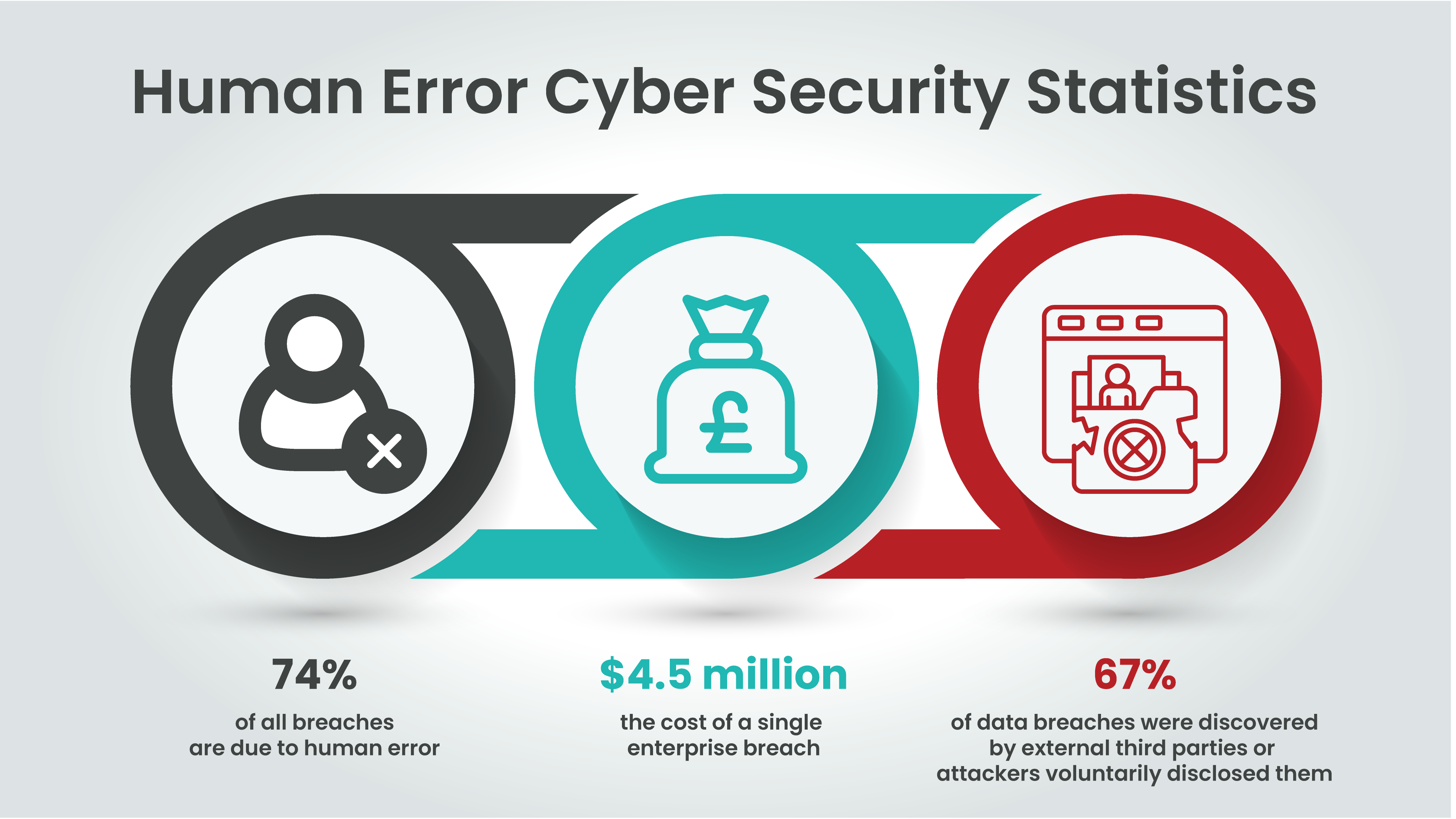
- Verizon’s Revelations: Human error was implicated in 74% of all breaches, highlighting its pervasive nature. From social engineering tactics to the misuse of privileges, human actions have significantly contributed to cyber security vulnerabilities
- Financial Implications: The financial impact is substantial. According to an IBM report, the cost of a single enterprise data breach soared to $4.5 million between March 2022 and March 2023. Organisations not using AI and automation faced even higher costs, with breaches averaging $5.4 million
- Discovery Dynamics: 67% of data breaches were discovered by external third parties or when attackers voluntarily disclosed their actions, indicating serious gaps in internal oversight
Understanding the Spectrum of Human Error in Cyber Security
Recognising the complex nature of human errors and the various categories that introduce vulnerabilities allows businesses to proactively strengthen their defences and mitigate risks effectively.
Simple Oversights
Employees handle numerous tasks daily, and simple oversights can become a significant concern, often driven by factors such as:
- Information Overload: The flood of notifications, emails, and alerts can desensitise employees, leading to crucial security warnings being overlooked or dismissed
- Time Constraints: In high-pressure environments, the urgency to complete tasks quickly may overshadow adherence to security protocols, increasing susceptibility to errors
- Lack of Awareness: Insufficient training or awareness programmes can leave employees ill-equipped to recognise and respond to potential threats
Social Engineering
Social engineering showcases the cunning strategies cybercriminals use to exploit human vulnerabilities. This deceptive approach includes a range of tactics, such as:
- CEO Fraud: Cybercriminals impersonate senior executives, leveraging authority and urgency to manipulate employees into unauthorised actions, like transferring funds or disclosing sensitive data
- Phishing Expeditions: Attackers use deceptive emails, messages, or phone calls to lure individuals into divulging confidential information, exploiting trust and familiarity to facilitate breaches
- Pretexting and Baiting: Beyond conventional phishing, pretexting involves creating fabricated scenarios to extract information, while baiting tempts individuals with false promises or rewards, further entangling them in malicious schemes
Misuse of Privileges
While external threats receive considerable attention, internal vulnerabilities from privilege misuse require robust oversight mechanisms. This category includes:
- Intentional Exploitation: Malicious insiders may deliberately abuse their elevated access levels, compromising systems and data integrity for personal gain or malicious intent
- Negligent Actions: Inadvertent misuse, such as accidentally modifying critical configurations or accessing unauthorised data repositories, highlights the need for stringent access controls and monitoring mechanisms
- Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) Violations: Failing to adhere to PoLP guidelines increases the attack surface, granting individuals excessive permissions that can be exploited by adversaries
The Consequences of Human Error
Human error in cyber security can trigger a cascade of consequences that affect various aspects of an organisation. Understanding these repercussions is crucial for businesses to grasp the full scope of potential damages and strategise effectively to mitigate risks.
Intellectual Property (IP) Loss
- Strategic Implications: Breaches that extend beyond immediate financial impacts can lead to unauthorised access or theft of invaluable intellectual assets. When competitors gain illicit access to proprietary data, it undermines a company’s unique selling propositions and erodes its competitive advantage in the marketplace
- Innovation Stagnation: The compromise of research, development, or proprietary technologies stifles innovation. Competitors may exploit stolen IP to replicate or surpass existing products, diminishing the original innovator’s market position
Regulatory Repercussions
- Financial Penalties: Non-compliance with stringent data protection regulations exposes businesses to substantial fines, draining financial resources and jeopardising profitability. Regulatory bodies worldwide impose hefty sanctions to enforce adherence, emphasising the need for robust compliance frameworks
- Legal Battles and Operational Constraints: Beyond monetary penalties, non-compliance can lead to protracted legal battles and stringent operational restrictions. Regulatory agencies may impose corrective measures, audits, or oversight mandates, limiting organisational agility and flexibility
Reputational Damage
- Customer Distrust: News of a security breach can spread rapidly. A tarnished reputation erodes customer trust, diminishing brand loyalty and engagement
- Stakeholder Scepticism: Beyond customer trust, breaches can instil scepticism among stakeholders, including investors, partners, and vendors. A compromised reputation may deter prospective partnerships, investments, or collaborations, hindering organisational growth and diversification efforts
- Long-term Growth Impediments: The combined effect of diminished customer trust, stakeholder scepticism, and reputational damage poses significant long-term growth challenges. Organisations must invest considerable resources and time to rebuild trust, often requiring comprehensive rebranding, marketing initiatives, and customer engagement strategies
How to Prevent Human Error in Cyber Security: A Multi-Faceted Approach
Effective cyber security requires a proactive, layered strategy that tackles the root causes of vulnerabilities. As human error remains a predominant threat vector, organisations must adopt a multi-faceted approach to mitigate risks effectively. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown of key strategies:
Comprehensive Training Programmes
- Knowledge Enhancement: Establish robust training programmes that educate employees about emerging cyber threats, common pitfalls, and best practices. By fostering a culture of continuous learning, employees become the first line of defence against potential breaches
- Vigilance and Responsibility: Encourage a heightened sense of responsibility among staff members through regular cyber security awareness sessions. By equipping them with the requisite skills and knowledge, organisations enable employees to recognise, report, and mitigate threats proactively
- Simulated Phishing Exercises: Conduct regular simulated phishing exercises to assess employees’ susceptibility to social engineering tactics. Analysing the results allows organisations to tailor training programmes effectively, addressing specific areas of vulnerability
Implement AI and Automation
- Real-Time Monitoring: Use artificial intelligence (AI) and automation to monitor organisational networks, systems, and endpoints in real-time. Advanced algorithms can detect anomalies, unauthorised access attempts, or suspicious activities, triggering immediate response protocols
- Automated Threat Mitigation: Deploy automated systems that can pre-emptively identify and neutralise threats without human intervention. From malware detection to intrusion prevention, automation strengthens cyber security defences, minimising the risk of human error
- Predictive Analysis: Utilise AI-driven predictive analytics to anticipate potential vulnerabilities or emerging threat vectors. By analysing patterns and trends, organisations can proactively fortify defences, staying ahead of cybercriminals
- Automated Patch Management: Implement automated patch management to ensure systems and applications are consistently updated with the latest security patches. This simplifies the process and reduces the risk of vulnerabilities being exploited
Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP)
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement a role-based access control framework that aligns with employees’ job responsibilities. By granting minimal necessary permissions, organisations mitigate the risk of unauthorised access, data leakage, or inadvertent errors
- Access Reviews: Conduct regular access reviews and audits to reassess and recalibrate user permissions. By aligning access rights with current job roles and responsibilities, organisations can maintain the principle of least privilege effectively
Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
- Real-Time Surveillance: Establish a robust monitoring infrastructure that tracks system, network, and user activities in real-time. Continuous surveillance enables organisations to detect and respond to anomalies promptly, minimising potential damage
- Vulnerability Assessments: Conduct regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing exercises to identify weak points in existing security frameworks. By proactively addressing vulnerabilities, organisations can fortify defences and pre-emptively thwart potential breaches
Conclusion
Human error is a significant challenge in cyber security. By understanding its nuances, implications, and mitigation strategies, businesses can strengthen their defences. With relentless cyber threats, proactive measures, continuous education, and technological advancements are crucial. Embracing a comprehensive approach that addresses human vulnerabilities while leveraging technological innovations is essential. Remember, in the battle against cyber adversaries, knowledge, vigilance, and adaptability are your strongest allies.
Simplify Your Cyber Security Journey
Human error in cyber security can be complex. We make it simple. Understand and implement a robust cyber awareness and training programme with ease.
Contact OneCollab today to develop a tailored cyber security strategy. Our Managed Services ensure the safety of your intellectual assets, regulatory compliance, and stakeholder trust with expert guidance and solutions.
